
Citizen science
Hydrological models
In-situ monitoring
Water Information
system
Water treatment
plant optimization
Early warning
system
Catchment risk
assesment
Hydrological models
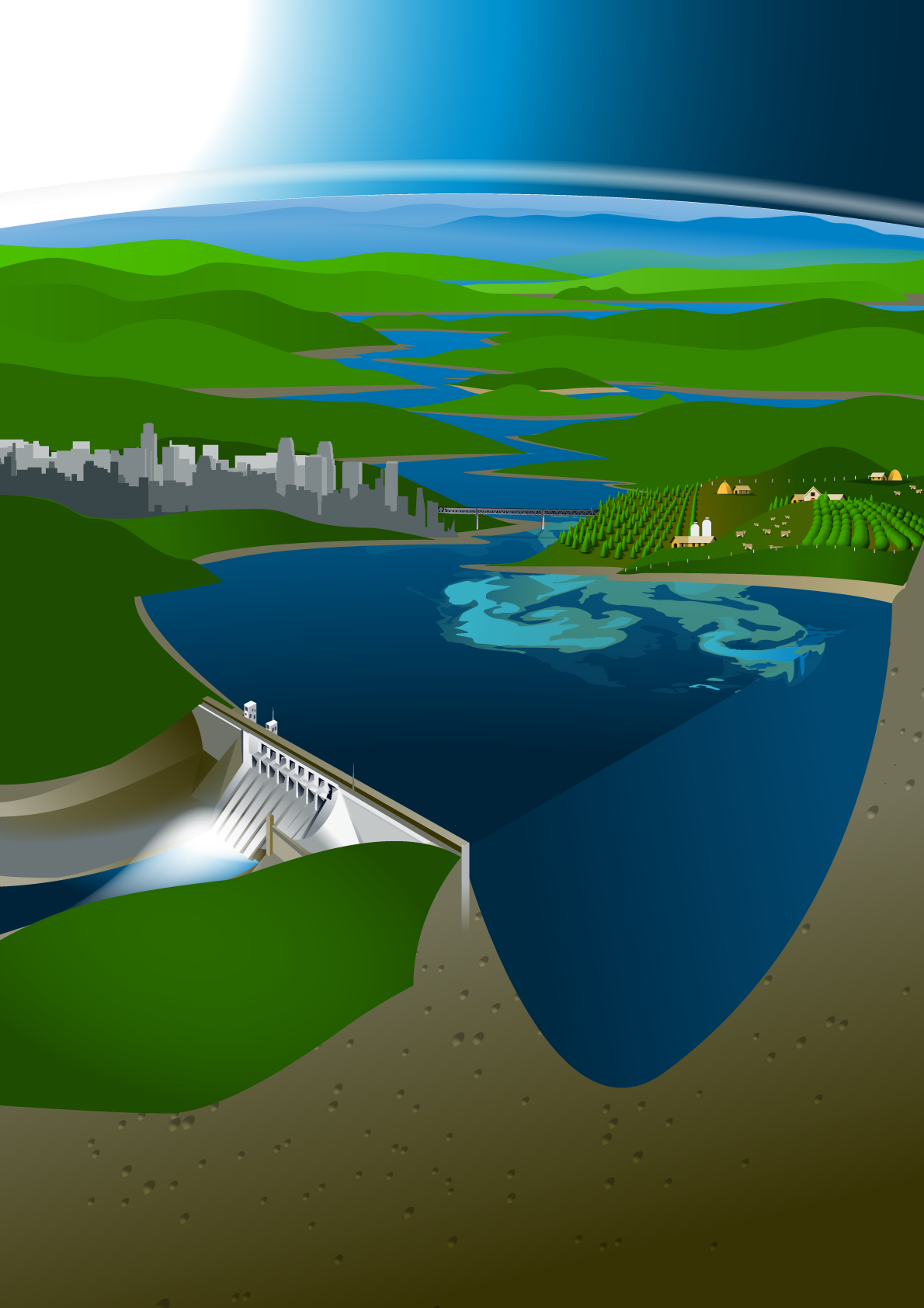
Hydrological models provide forecasts for the next 10 days for the quantity and quality of water that reaches the reservoir, e.g. predicts the concentration of pollutants in the water. These forecasts are generated by the open-source HYPE model, which is a semi-distributed hydrological model that provides forecasts of river discharges, water temperatures, nutrient and sediment loads in the catchments. Inside the reservoir, 3D hydrodynamic and ecological modelling is performed based on the Delft3D Suite model in order to estimate water elevations and velocity fields as well as critical water quality parameters for the next 10 days (various algae species, nitrogen, phosphorus, dissolved oxygen, suspended sediment, etc.). In addition to the ECMWF deterministic and probabilistic meteorological forecasts, high-resolution Numerical Weather Prediction models complement the meteorological input for hydrological forecasting applications.
In-situ monitoring
A broad range of monitoring devices can be seamlessly integrated in the operational platform of SPACE-O including:
- Local meteorological stations
- Floating water quality stations and sensors
- Water level monitoring equipment
- Any signal collected through the supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) system of the Water Treatment Plant.
Data are collected, processed and stored in the SPACE-O central database through an open Application Programming Interface (API). Stored datasets can be used directly for assimilation in the water quality models and the Decision Support System, or simply to view in the Water Information System.
Citizen science
The "Improve my Water" tool enables citizens to report non-emergency local problems such as leaks, illegal activities, abnormal findings, etc., regarding the area in and around a lake, reservoir, and any other area of interest for a water manager/operator. The submitted issues are displayed on the city’s map. Users may add photos and comments. Moreover, they can suggest solutions for improving the city’s/municipality’s/region’s/etc. water infrastructure. Through this service the competent authorities enable citizens and local actors to take action to improve the provided service and to optimize the performance.
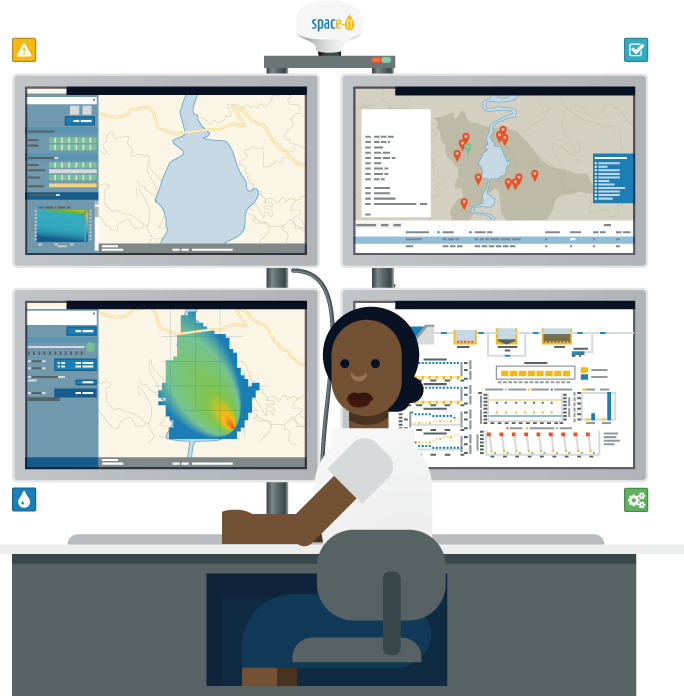
Precise forecasting
The Early warning system can be used to access information on possible threats to the water system. The system issues warnings on:
(a) the stratification and mixing patterns of the reservoir (e.g. thermocline depth, lake number etc.)
(b) physico-chemical parameters such as nitrate concentration and turbidity,
(c) phytoplankton-related metrics such as the chlorophyll-a concentration, the biovolume of cyanobacteria, the species evenness index, and the bloom intensification index, and last but not least (d) the extreme river discharge values, whereby the hydrological parameters are based on critical thresholds for sub-basins discharge corresponding to 2, 5 and 30 years return periods..
The warnings are closely related to the function of the downstream water infrastructure and, therefore, they refer specifically to the vicinity of the water abstraction points.
Satellite observation
Satellites can observe a broad range of environmental parameters. SPACE-O uses Sentinel-2 A/B and Landsat 8 satellite open access data to observe and forecast water quality. These satellites have a resolution of 10-30 meters.
Commercial satellites can be added as well, improving the resolution up to 2 meter.
Satellite data is processed using sensor independent and state-of-the-art physics based Modular Inversion and Processing System (MIP), developed by EOMAP.
Harmful algae
Harmful Algae Blooms are increasingly devastating water resources. High nutrient loads, warm temperatures and long resident times increase the risks for such algae blooms.
Peak rainfall events not only wash nutrients into water systems, but also other suspended solids that cause high turbidity in water bodies. Both, high turbidity and harmful algae blooms pose severe challenges for water treatment plants. Forecasting those events, helps to prevent them and adapt operations accordingly.
Users
Users of this platform include bulk water managers, drink water utilities, dam operators, catchment authorities and researches.
Satellite based measurements cover water quality parameters: chlorophyll-a, turbidity, Z90, secchi depth, and water surface temperature. These parameters are indicators for harmful algae blooms indicator, amongst others.
Water treatment plant
Drinking water treatment plants can use the SPACE-O tools to forecast water quality in their intake water resources, to inform their water resources management, and to optimize their water treatment processes. The Water Treatment Plant Optimization tool relies upon a credible emulator of the system processes. This emulator is a series of machine-learning algorithms, which describe the performance of each treatment stage separately under varying raw water characteristics and operating scenarios.






 Citizen scienceHydrological modelsIn-situ monitoring
Citizen scienceHydrological modelsIn-situ monitoring Water Information
Water Information Hydrological models
Hydrological models

 Harmful algae
Harmful algae Water treatment plant
Water treatment plant








